What is a 404 error?
A 404 error page is displayed on a website when a server cannot find the requested URL. This typically happens when the page has been moved or deleted, or the URL was mistyped. It is an HTTP status code indicating that the server could not locate the resource.
Why is it called a 404?
In short, the page is called a 404 page because it displays an HTTP 404 status code. This error is shorthand for ‘The resource you are looking for cannot be found’.
HTTP 404 is a status code
The status code tells you whether your request to display a web page was successful. If the request fails, the code will help you understand the issue. This is how it works: whenever a page or resource is requested on a website, the underlying server processes the request and presents an answer. The answer contains headers and a data part. The data part is the requested document, while the headers contain metadata like file size, last modification time, and more. Part of the headers is your HTTP Status Code: HTTP, followed by a 3-digit number.
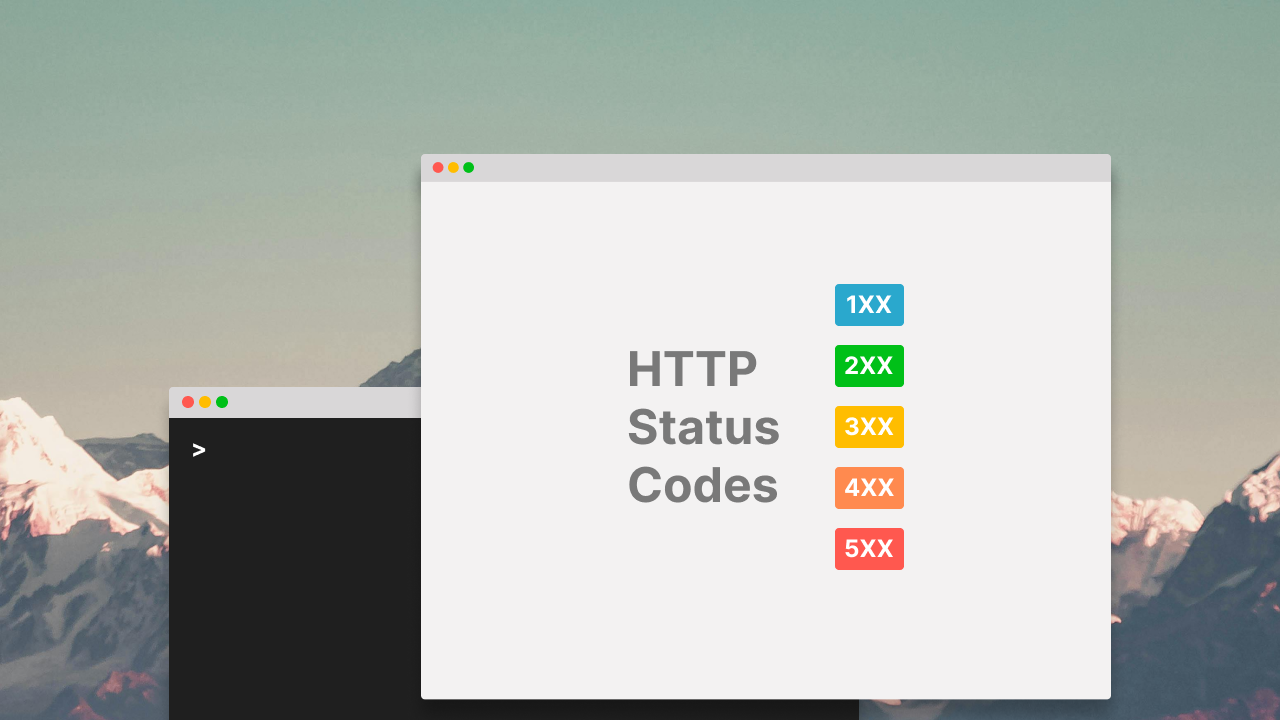
Types of HTTP status codes
Status codes are grouped into five categories:
- 100-199: Informational statuses
- 200-299: Successful statuses
- 300-399: Redirection statuses
- 400-499: Client error statuses
- 500-599: Server error statuses
A 404 page is called this because the “Resource Not Found” status code is 404. It is classified as an error.
How to interpret an HTTP error message
When the HTTP status code is an error, the message will contain a number in the 400 or 500 range. The number tells you something about the potential culprit of the error.
- In the 4xx range, it’s expected the error happened on the client side. In most cases, the browser made a bad or wrong request.
- If the number is in the 5xx range, the error results from something on the server side. Possible causes are a database error, an overloaded server, a configuration error and so on.
(Note: this isn’t always true, as a request could end in a 404 error when the server has a misconfiguration and is missing files, for example.)
How does someone land on a 404 error?
A web visitor lands on a 404 error page by clicking on a link that points to a web page that doesn’t exist. We call this a broken link or a dead link. This could be on your own website. In this case, we call it an internal link. If the link is on someone else’s website, pointing to a page on your website, it’s an external incoming broken link. See our guide on monitoring broken links for more information on how to deal with that. A more rare case is that someone is guessing the name of a page, or made a typo in the complete URL.
Next: make your 404 page better
Now that you understand what a 404 error is, it’s time to apply that knowledge to the user experience of your web visitor. To help you out, we have created a list of 6 things you can do right now to make your HTTP 404 page better.
Go to next article: 6 ways to make your HTTP 404 page better
This article is part of The ultimate guide to 404 pages.