How to know if your website has 404 errors
Website visitors get an HTTP 404 error when the web page that they are to access is not available. The link to the resource is broken. (Not sure what this means? Then read our previous blog article first.) So how can you know if your visitors are getting an HTTP 404? Clicking every page on your website is too much work. That’s why the best way to find HTTP 404s is by scanning your website for broken links.
1. Scan for broken links
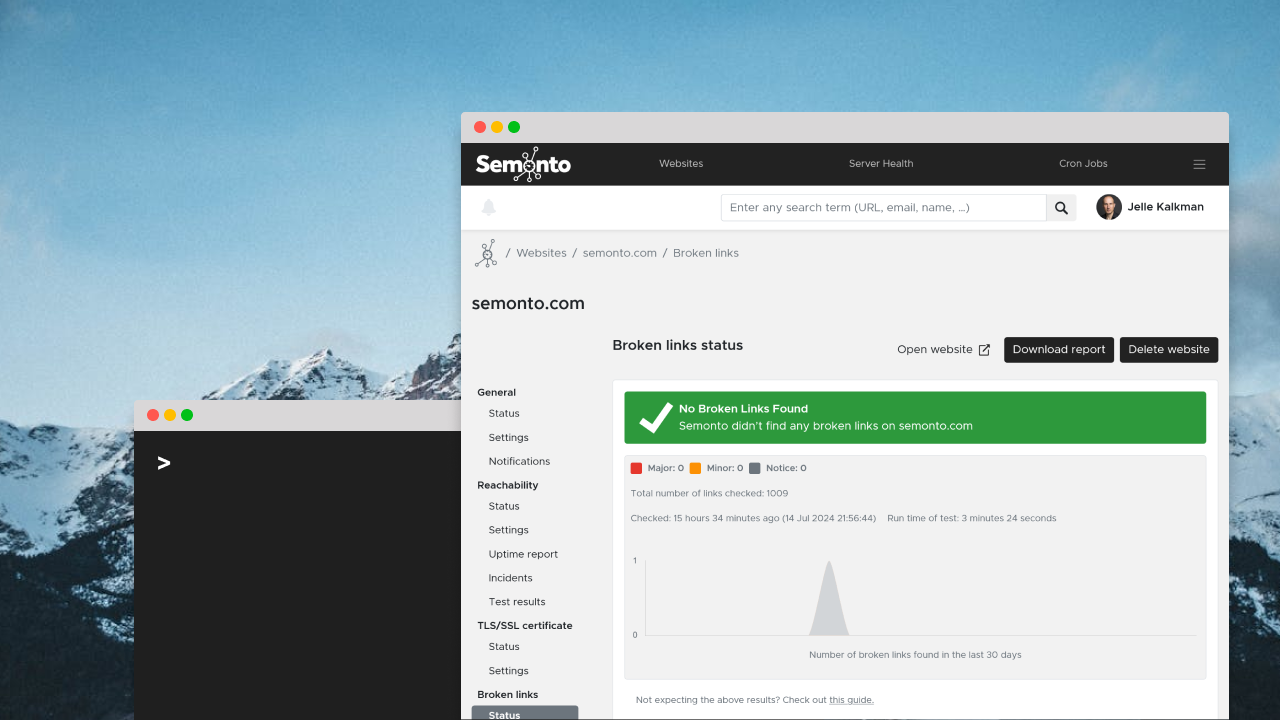
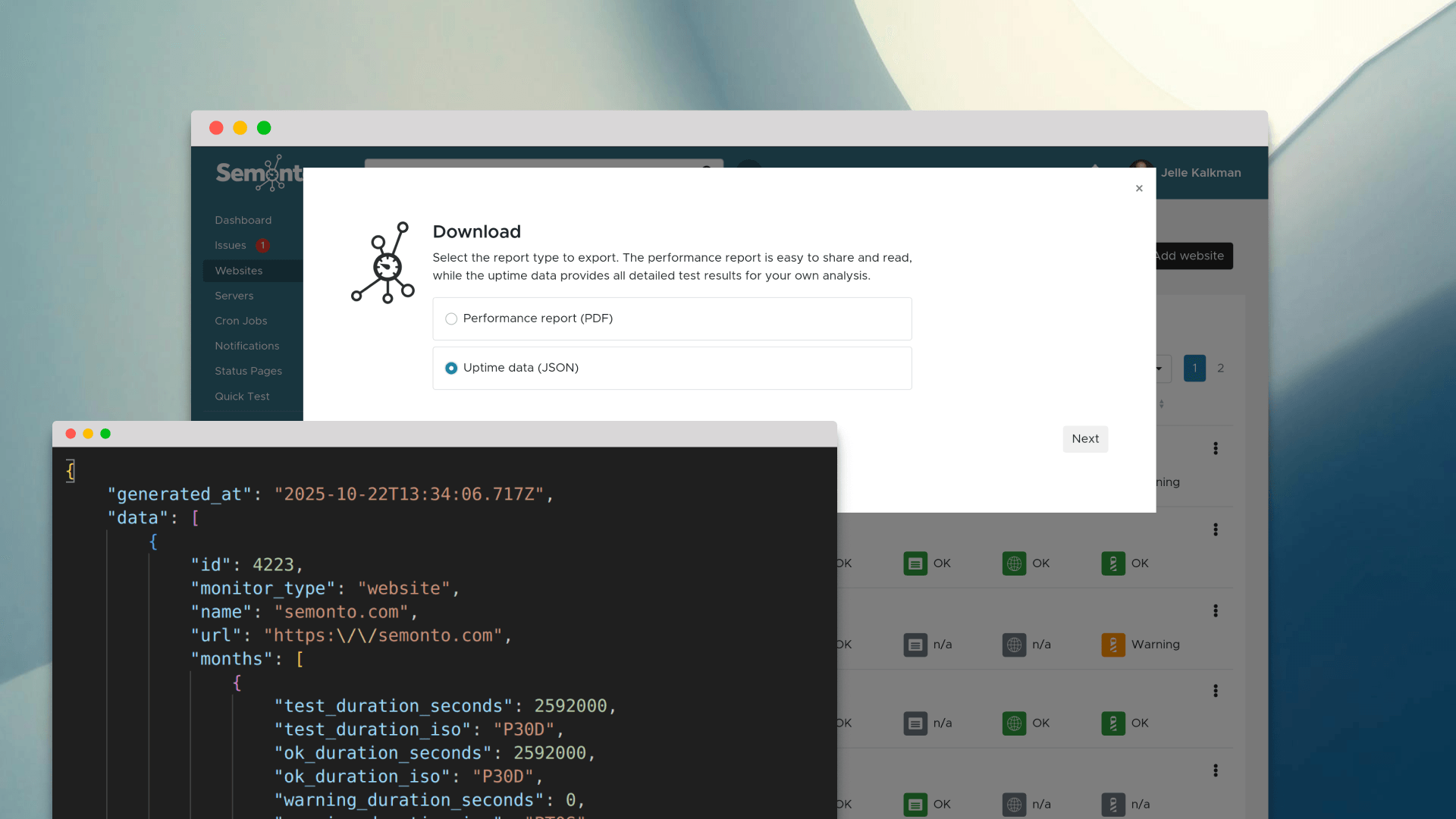
Be sure to scan your website for any broken links. Also, scan any link to external websites, as you don’t want to drop your website visitors on pages that don’t exist elsewhere. It’s not enough to scan when you make changes on your website or when releasing the website, as links can break for multiple reasons. To cover this, ensure to scan periodically. Links to external websites can break anytime. Semonto can help you scan for broken links smoothly without installing anything. If you want the complete process beyond 404 prevention, use our broken link monitoring best practices guide.
2. Keep an eye on Google Search Console
Google Search Console has a section about broken links. It’s different from the results from those of a scanner like Semonto. Google will show the pages it knows from its index that don’t exist any more. Ideally, you add a redirect for those pages to the new page or similar page. More info in our Google Search blog article.
3. Add a tracker on your 404 page
As explained, you still should have a 404 page and should try to offer the best experience for your website visitor so they are not at a dead end. Be sure to add a tracker on this page so you have a better overview of when 404 pages are being triggered. Also, check the context, such as which pages were requested, which page was linked to this page, and more.
4. Give Semonto a try
Semonto has a broken link monitor that will keep an eye on your website 24/7 and send you a message whenever a broken link is found. Do you know if you have any broken links? Just try Semonto: We offer a 30-day trial with no credit card required, no strings attached, and no installation required. Just enter your website URL, and you are ready to go.
Lastly: It’s not only about pages
When mentioning links, it’s easy to only think about web pages. However, pages are not the only resources that could be missing, resulting in a 404 page. Other resources, such as files, images, and more, could also be missing. Be sure to take this into account when monitoring your website. (Semonto will list these, too, when you are monitoring for broken links).
PS: This article is part of our ultimate guide about 404 errors. If you liked it, you might want to read the other chapters.