Setting up cron job monitoring
A guide on monitoring non-webservers or periodical scripts with Semonto.
You can use cron job monitoring to monitor servers that are not accessible over the internet, database servers or behind a firewall for example. Consider it like measuring the heart rate of a server. You can also use a cron job monitor for monitoring periodical scripts such as backup-tasks.
The idea is actually quite simple: Your server needs to give a pulse to our server (just by calling a specific url). If your server does not give a pulse on time, Semonto will alert you.
Creating a cron job monitor
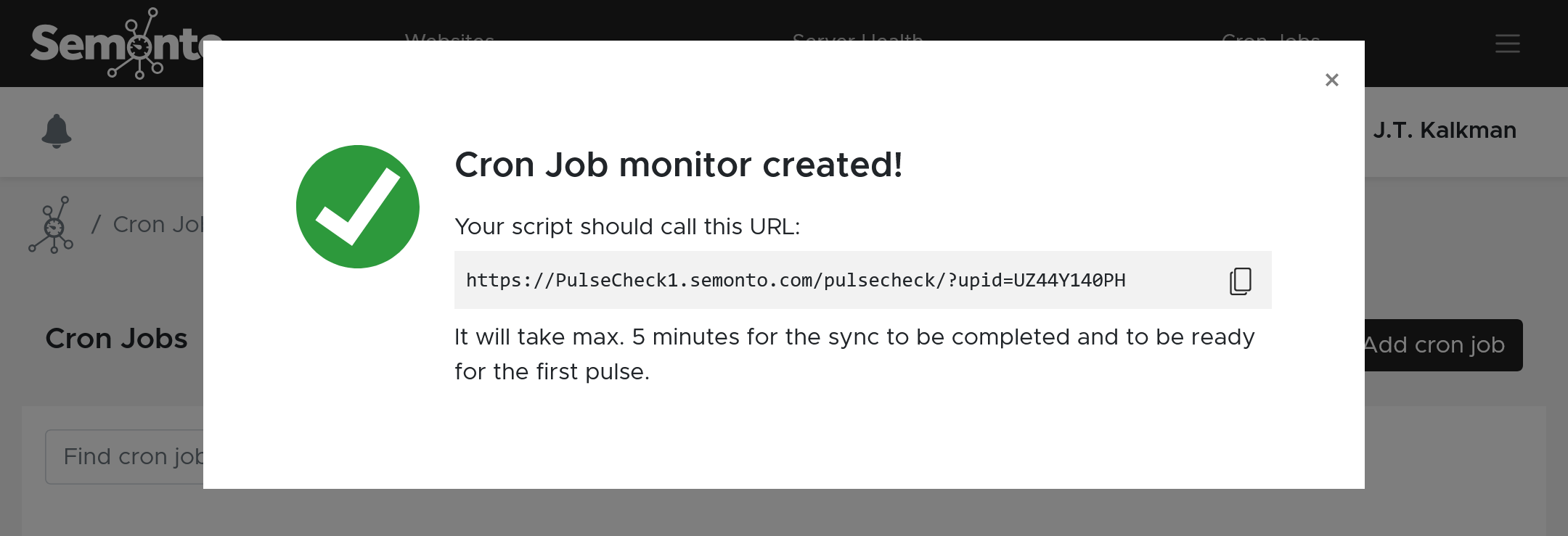
When you create a cron job monitor, Semonto will create a unique URL which you need to call on your server.
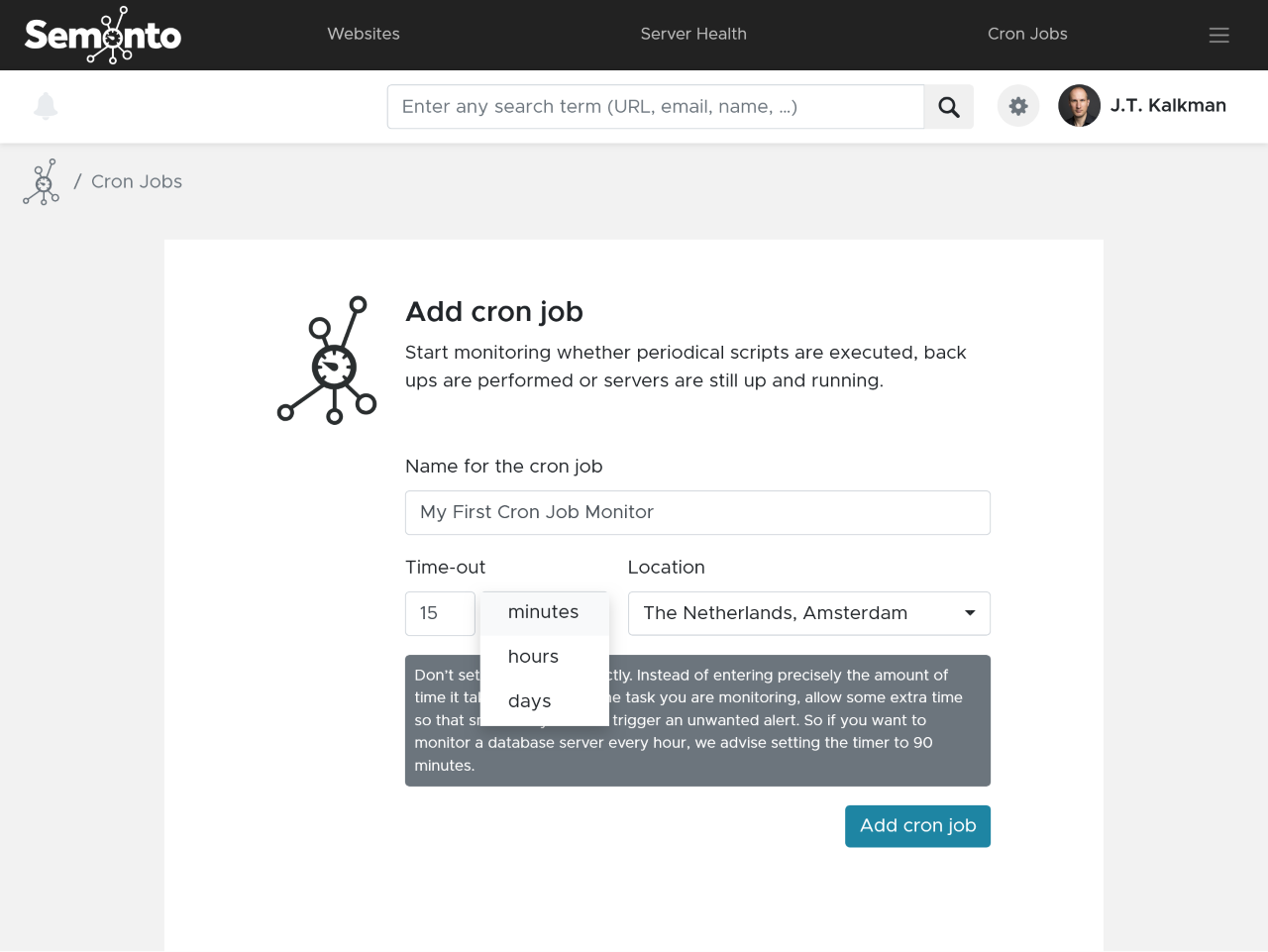
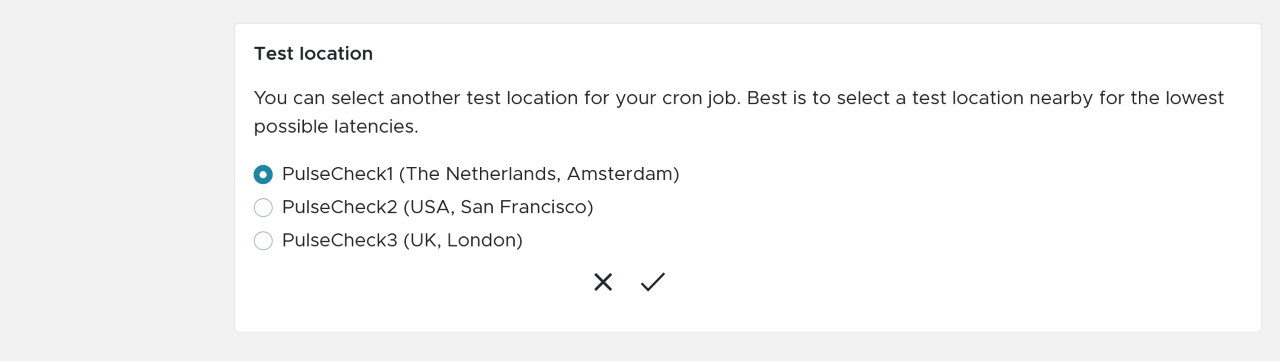
You can specify the time-out immediately and you can select a specific server from Semonto that should check for the pulse by your server. When you set the time-out, make sure to provide a bit of overlap. For example when you use a cron job monitor for a back-up script, set the interval to 25 hours when you back up daily or when you monitor a database server every hour, set the time out to 90 minutes.
Cron job monitor settings
When creating a cron job monitor you only have to provide a name and a time out, the time in which the next pulse should be received by Semonto. We also provide the option to select a specific server, best is to select the server nearby.
Alerting
It is important to assign at least one Contact Group to a cron job monitor to alert someone when it expires. This can be done in the notification tab in the monitor.
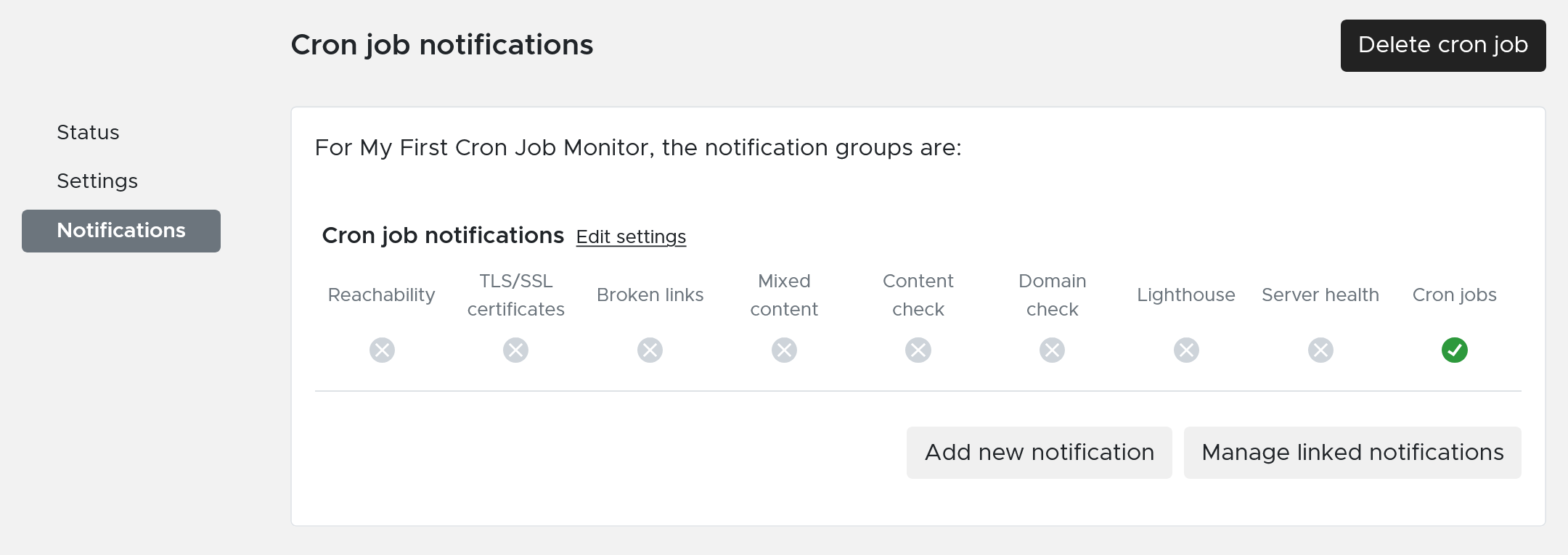
You can assign multiple contact groups to a cron job monitor to have fine grained control who to contact when the pulse expires. You can read more on Contact Groups this guide.
Details
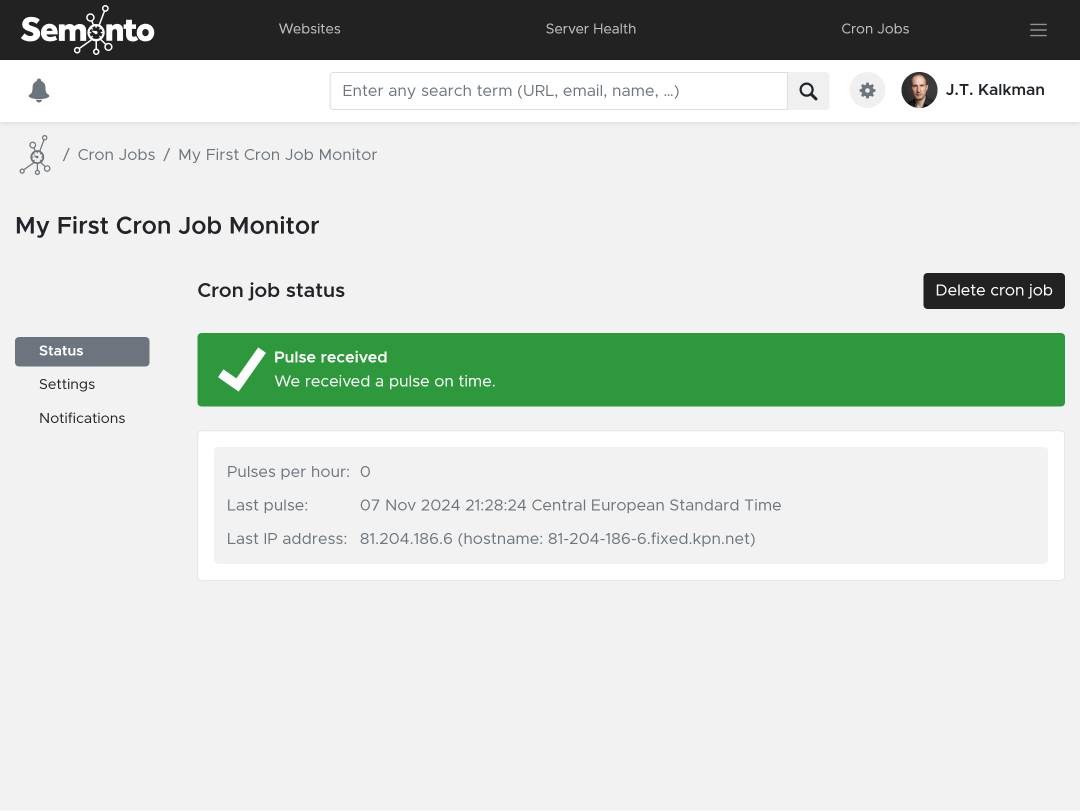
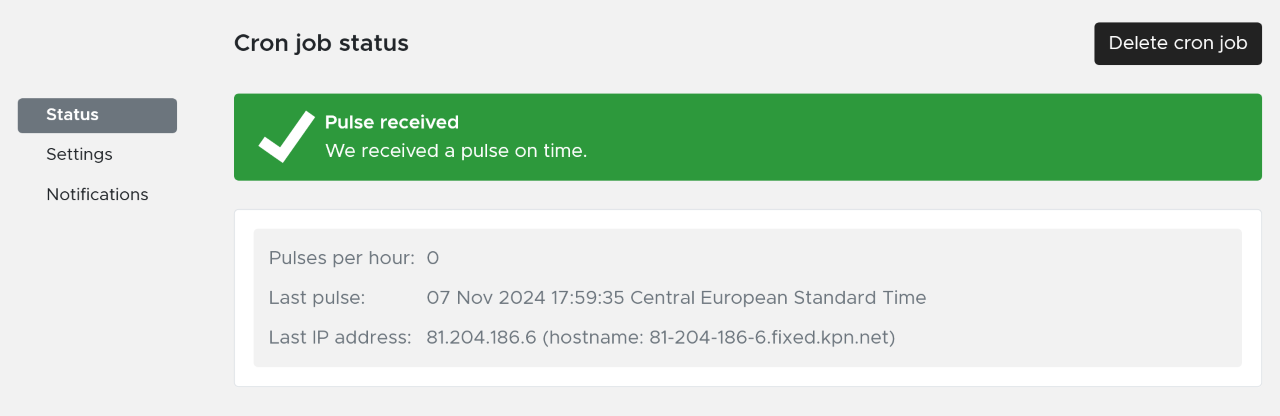
In the status tab you can find all the information from the cron job monitor. Also the IP-address from the last pulse and the frequency of the pulses.
Examples
If you have a backup-script that runs daily and you would like to be alerted when the backup-script did not run for more than 25 hours.
Create a new cron job monitor and Semonto will generate a new URL to call, for example:
https://PulseCheck1.semonto.com/pulsecheck/?upid=RA122X93W2When the cron job monitor has been created and is ready (this can take up to 15 minutes and can be checked at the details page of the monitor), you can integrate a call to this URL in your script. Your script needs to call this URL when installed on your server and needs to call this URL within the time out.
For example in CURL:
curl --connect-timeout 5 -f "https://PulseCheck1.semonto.com/pulsecheck/?upid=RA122X93W2"For example in PHP:
<?php $url = "https://PulseCheck1.semonto.com/pulsecheck/?upid=RA122X93W2"; $result = file_get_contents($url); //check $result ?>Resolving issues
Results from calling this URL can be:
0: which means everything is okay.
Error 144: in this case you need to check if you have the correct URL to call and if the cron job monitor is synced yet (you can check this in the status tab of the cron job monitor).
When you need any assistance on setting up a cron job monitor for your server, feel free to contact us at info@semonto.com.